背景
通常而言,C/C++制作二维图形的绘制程序采用GDI或者GDI+已经足够,不论是绘制的效率还是绘制图元的类别。制作跨平台的程序的主要目的是将已有的绘制程序转移到移动端,以安卓为例,可以使用android studio编译出的.so文件,进而做二次开发。
如果是仅仅制作一个apk文件,那推荐使用现有的封装好的平台,如cocos2dx,同样的代码可以在安卓、IOS/MAC、Windows等平台编译出可执行程序。但是这里的需求要把绘制模块独立出来(不能把场景之类的东东带上),数据访问形成jar包供二次开发使用。从cocos2dx中分离绘制 VS 另写一个绘制模块,选择了后者。
既然跨平台,首选当然是openGL,悲催的是,接触后发现移动端不支持很多原生态的函数,诸如glBegin glLineStipple这样的函数都不支持,而不得不使用GLES。以下是一篇介绍从openGL转换到ES的文章:
https://pandorawiki.org/Porting_to_GLES_from_GL
即便是最简单的绘制线,也不得不使用glDrawArrays这样的函数来执行了。
绘图简介
这个系列将用几篇文章来介绍近期GLES学习和使用的心得。绘图程序需要考虑的因素有:
(1)绘制效率,库文件编译出后需要在手机端二次开发使用,因此需要保证绘图效率;
(2)绘制图元,包括点、线、多边形(含不规则多边形)、文字;
(3)绘制顺序,所有的图元有先后顺序,保证叠加的次序和读取的数据一致;
(4)图元特性,例如线宽、线型、符号等的支持;
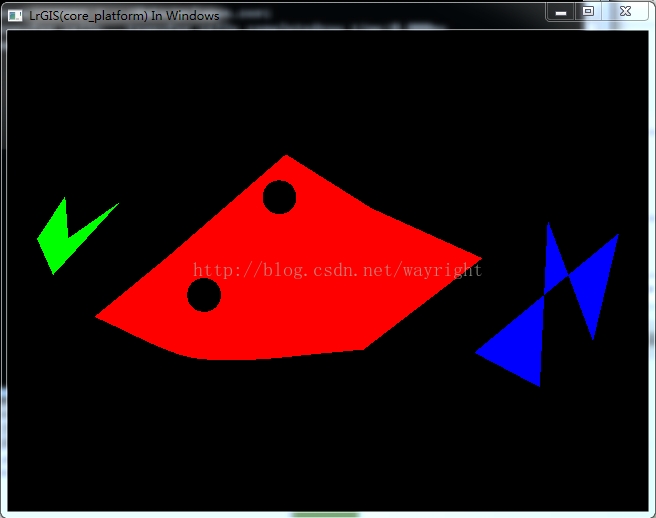
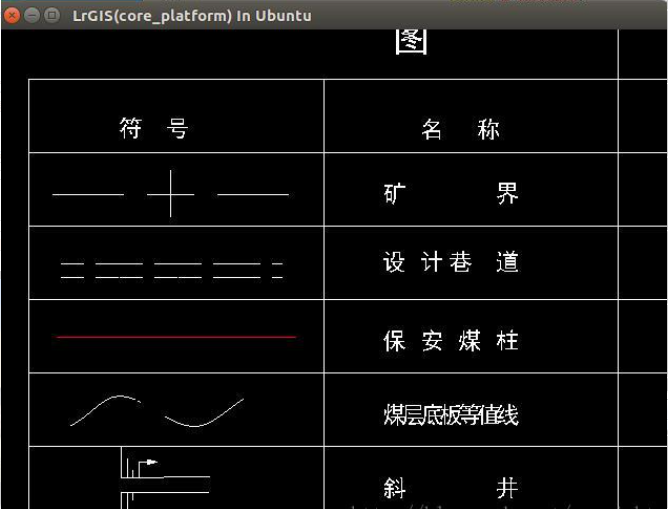
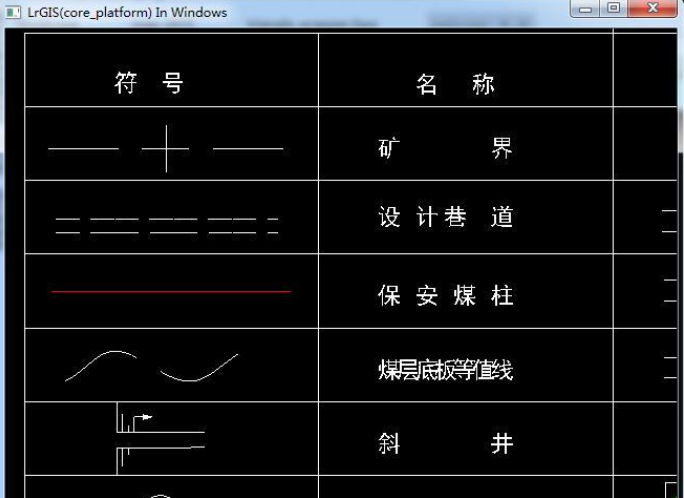
效果图
通过这一段时间的尝试,得到了如下的展示效果,拥有较高效率且支持主要图元的跨平台程序。
着色器
学习使用GLES,首先要写着色器。
与OpenGL ES1.x渲染管线相比,OpenGL ES 2.0渲染管线中“顶点着色器”取代了OpenGL ES 1.x渲染管线中的“变换和光照”;“片元着色器”取代了OpenGL ES 1.x渲染管线中的“纹理环境和颜色求和”、“雾”以及“Alpha测试”。 这使得开发人员在使用OpenGL
ES 2.0API进行开发时,可以通过编写顶点及片元着色器程序,来完成一些顶点变换和纹理颜色计算工作,实现更加灵活、精细化的计算与渲染。
以上内容转载自:
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_923fdd9b0102vbe0.html
文章对着色器做了一些介绍,在GLES的使用步骤为:glCreateProgram->glAttachShader->glLinkProgram->glUseProgram。在之后使用纹理之后才知道,一个程序里可能同时存在多个program,在绘制不同对象时需要切换使用glUseProgram。在出现错误的时候错误日志非常关键,调试的时候发现同样的shader代码在windows平台可以绘制,但是在ubuntu中就无法显示,错误日志可能提示语言的版本不支持。这些错误与系统GPU有关系。以下为包含着色器的Program封装,包括常规程序和带纹理的程序。
1 |
|
代码编写参考了:
http://blog.csdn.net/hb707934728/article/details/71486631?locationNum=4&fps=1
主要做的改动:
(1)着色语言,区分android,区分版本,区分坐标——尤其是z坐标引入保证深度测试能够生效(vec4 pos = vec4(_position, 1.););
(2)纹理程序继承自常规程序而非基础程序类;
(3)引入了变换矩阵(用于旋转缩放平移等运算);
VAO&VBO
随着OpenGL状态和固定管线模式的移除,我们不在用任何glEnable函数调用,而且也不会有glVertex、glColor等函数调用。这就意味着我们需要一种新的方式来将数据传输到图形卡以渲染图形。我们可以采用VBO,或者是在OpenGL3以上版本引入的新的特性,叫做VAO。通过它,我们可以把顶点数据和颜色存储在不同的VBO中,但是在同一个VAO中。对于法线数据或者其他的顶点信息也是一样。
VAO,是这样一种方式:把对象信息直接存储在图形卡中,而不是在当我们需要的时候传输到图形卡。这就是Direct3D所采用得方式,而在OpenGL中只有OpenGL3.X以上的版本中采用。这就意味着我们的应用程序不用将数据传输到图形卡或者是从图形卡输出,这样也就获得了额外的性能提升。
使用VAO并不难。我们不需要大量的glVertex调用,而是把顶点数据存储在数组中,然后放进VBO,最后在VAO中存储相关的状态。记住:VAO中并没有存储顶点的相关属性数据。OpenGL会在后台为我们完成其他的功能。
以上内容引用自:
http://blog.csdn.net/xiajun07061225/article/details/7628146
使用VAO和VBO更重要的原因在于提高绘制效率。在绘制线对象的时候,对现有的GDI和GLES的绘制效率做了对比,同样的4K条折线段绘制时间均在40~60ms。即相比GDI,GL并没有较大的绘制效率提升。
VAO、VBO使用心得
使用VBO和VAO之后,绘制时间基本为0。原因在于:坐标数据已经通过缓冲传入了GPU,通常看图的前提下,坐标数据改动的可能性很小;而原有的绘制在变换图形时,每次都对坐标数据做了转换(实际数据->屏幕数据),继而将转换完成的数据传到GPU,然后渲染。缺少了源源不断不断的坐标数据转换和切换,绘制效率也就提升了。
为了能够继续进行图形的变换(缩放、平移、旋转),引入附加矩阵(additionTransform),用来计算当前视图(currentViewContext)和原始视图(通常是全图时候的上下文:fullViewContext)比例关系。这样当进行缩放时,currentViewContext发生了变化,additionTransform = currentViewContext / fullViewContext,additionTransform传入第二篇中Program的开始函数即可实现变换。而原有的currenViewContext保留用于计算屏幕坐标和实际坐标转换。
坐标数据超过float能表达的范围怎么办?openGL和GLES中传递的数据通常都是float数据,而且有效数据仅6~7个,但是地理坐标数据通常都是需要十几位有效数据,如果在使用时直接将真实坐标数据传入VBO中,绘制出来的线段很可能是锯齿形状。所以在传递数据前,先以地图左下为参考原点做一次偏移再传入VBO,这样基本就能满足数据精度要求了。
代码
以下代码为几何VBO的管理类,负责创建VAO、VBO以及绘制。
1 | struct GeoVOBuffer |
粗略解释为:我们把所有的线坐标存入了GPU,GPU返回了一个ID(VAO)。在绘制的时候我们绑定这个ID,然后进行绘制,这些线就会被一次性全部画出。
为了管理不同类型的VAO,编写了一个vo的管理器,里面同时记录了一些使用VAO时需要的数据,如左下角偏移、Z深度等。
1 |
|
下面是一个线类型坐标转换到VAO的代码:
1 |
|
由于要求独个VAO的一次性绘制,不得不使用GL_LINES(GL_LINE_STRIP无法使用)。
多边形绘制
前三篇内容的基础上,可以绘制出如下的图形:
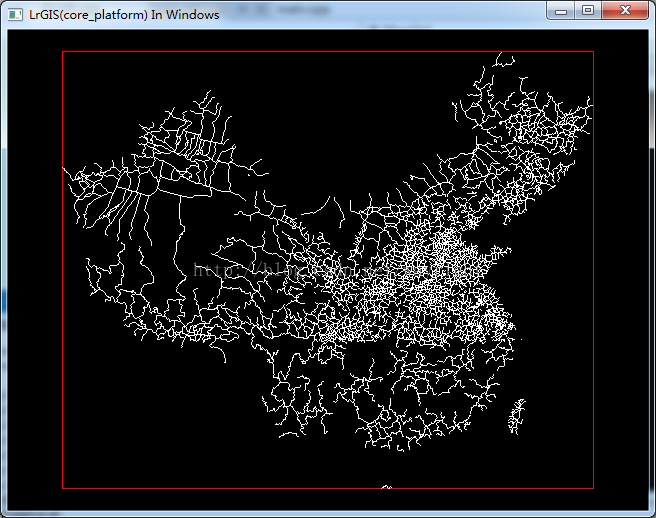
这一篇介绍如何绘制多边形。
(1)GDI通过API函数Polygon或者PolyPolygon就能够绘制不规则的多边形,包括自交带内洞,而GLES只能绘制三角形;
(2)多边形三角化有个开源的triangle.h,这里推荐下:http://compgeom.com/~piyush/scripts/triangle/triangle_8h-source.html
(3)三角化的时候要注意几个问题。多边形点中不可以有重复坐标点,否则会出错;多边形坐标点数不可过少,否则出错。
以下是多边形三角化的一个类:
1 |
|
有了这样的三角化类,就可以将不规则多边形(如凹多边形,带内洞多边形)转换为三角形,然后将三角形传递到VBO中。
1 |
|
这样多边形就能够渲染出来了!